Correct powder gun setting
Here is our new 2025 spray gun with 4 patents ! (in blue)
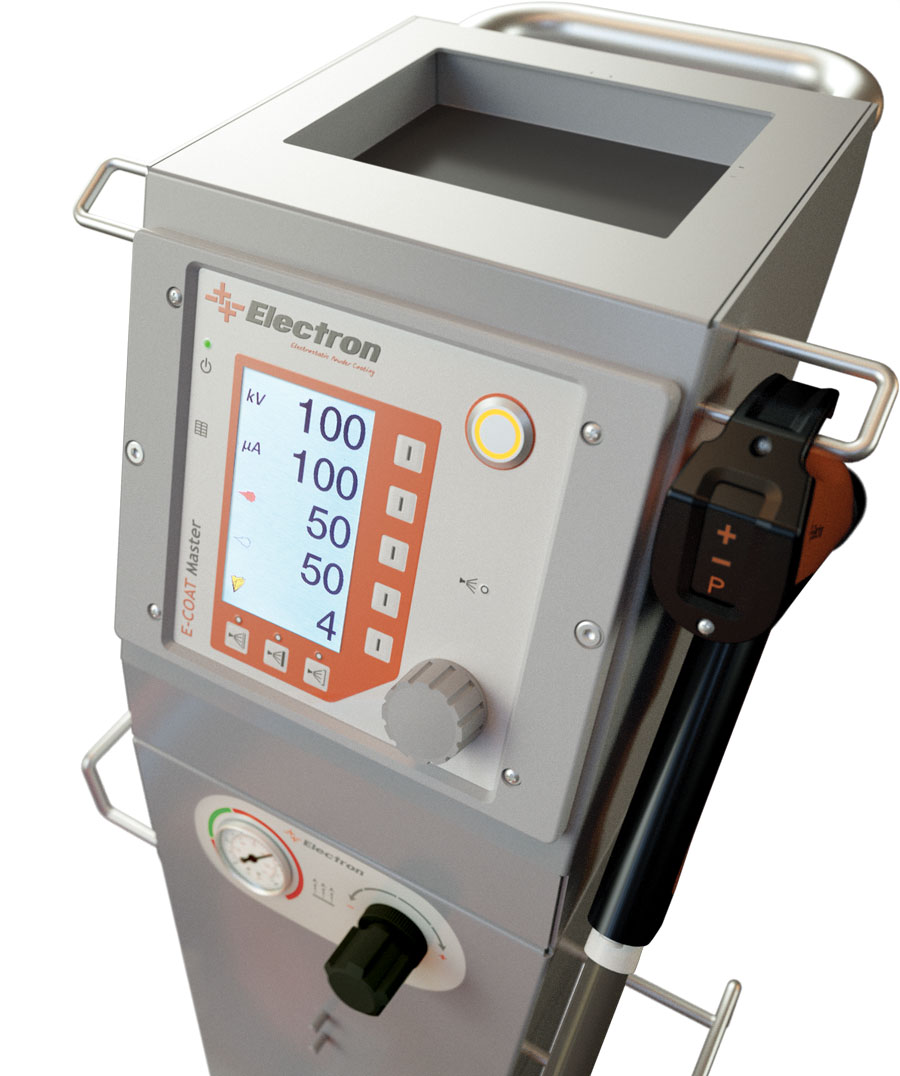


Quick keys
Generally with E=4 and % 60
3 quick keys for recipes (under the display)
Flat parts
Second layer
Complicated shapes
Understanding parameters
- kV = high voltage in kiloVolt, static friction
- µA = spray current in microamps
- E = total air = 4.0 Nm 3 / h (h = hour)
- % = Powder output rate, for example 60% coating 40% air
- Recipe # 3
kV - µA Relation
Automatic regulation of the load to the distance workpiece
Control unit recognizes the distance or workpiece surface and regulates kV and µA at that moment. If the gun tip is too close, the µA is reduced and vice versa.
High kV if:
The higher the setting, the stronger the charge / adhesion.
flat parts and for the outside of box-like parts.
Low kV if:
the more detailed and complex the part (inner surface) to improve transfer efficiency so that it penetrates to the corners
(more powder particles to the part) e.g.
- 50 kV with 20 to 40µA
- 50 to 60 air mixture %.
- increase the distance between the gun and the part
- to obtain a very uniform coverage on flat surfaces
1. Flat parts
Flat or first layer
100 kV / 100 µA set.
Recommended set area is 50 to 80 kV with 70 to 100 µA
3. Complicated shapes
Square edged workpieces: (outer surface)
100 kV / 22 µA set.
Works well with 90 kV and 22-35 µA
2. Overcoating or second layer / two-coat process
100 kV / 10 µA set.
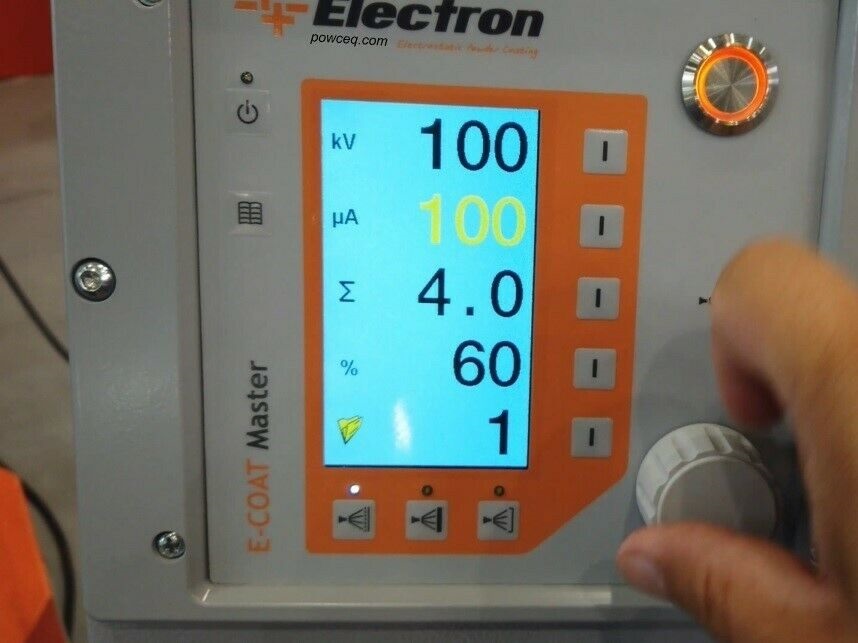

Coating Gun Setting values
Coating angular workpieces
kV 90 = 90,000 V
µA 35 = 3.5 x 10-5 A
E 4.0 Nm3/h or lt/min
% 60 = powder output
- = powder coating in spray air
Recipe no. 3
2. Overcoating or second layer / two-coat process
100 kV / 10 µA set.
The range of values for the second layer fluctuates between
- 100 kV with 10 µA and
- 80 kV with 10 µA
- 50 kV with 20 µA, even up to
- 20 kV with 30 µA
- First coating, for example, you can leave the KV setting at 80 kV
- second over-coating at 50 kV
- third over-coating at 30 µA, each with a limit of 10 to 30 µA.
If you notice reionisation, i.e. the inner corners are already electrostatically charged so that no further penetration of the powder is possible, you can reduce the KV and leave the microampere setting at the lower end of the range of 10 to 30 µA microamps.
Two-shift process doesn't work? More Tips
Here are a few tips
Sometimes important rules are overlooked.
Possibly increase the % of powder used.
1. Use the earthing tester
First layer 4 millimeters thick? Create a bare metal point on the part so that it can be grounded
2. Check powder coating values on manufacturers box
3. Does the first coat have stains, problems with significant peeling or rust breakage?
4. Cleaning the product surface
Powder Coating Equipment & Machine for sale
Worldwide easy delivery - new systems
Offers
receive password immediately
Info sheets PDF
No password required
Description and presentations
Documents
No password required
Product summary powder coating equipment
Click below on interested product ~ We ship anywhere, worldwide
 Nr.1 Coating gun: Pro M
Nr.1 Coating gun: Pro M Nr.2 Coating gun: Master M
Nr.2 Coating gun: Master M Nr.3 Booth FT2 & oven EL15
Nr.3 Booth FT2 & oven EL15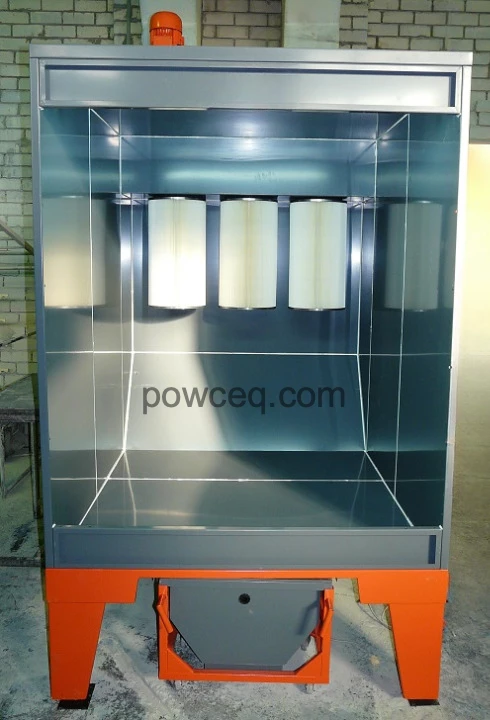 Nr.4 Booth FT3
Nr.4 Booth FT3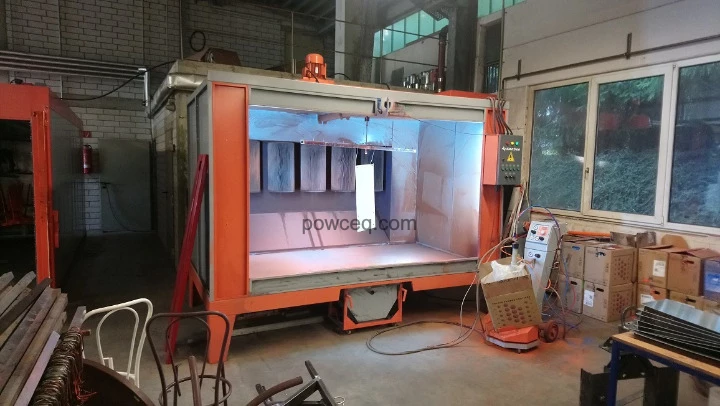 Nr.5 Booth FT5
Nr.5 Booth FT5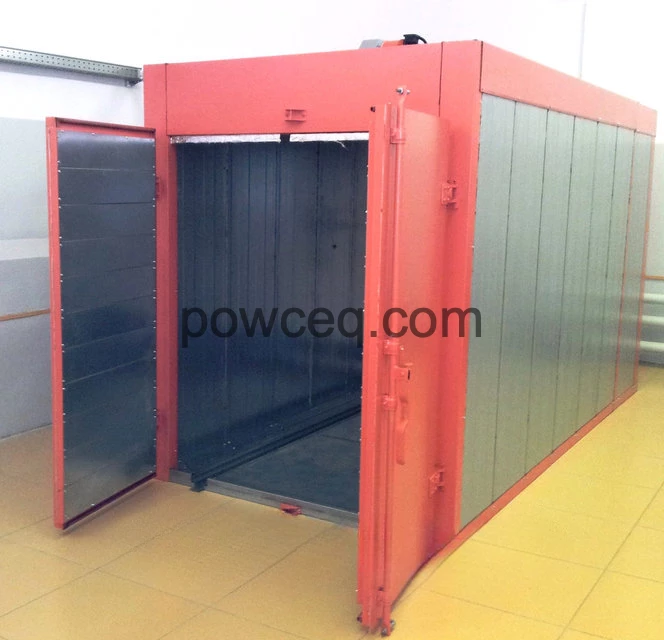 Nr.6 Oven electrical E3
Nr.6 Oven electrical E3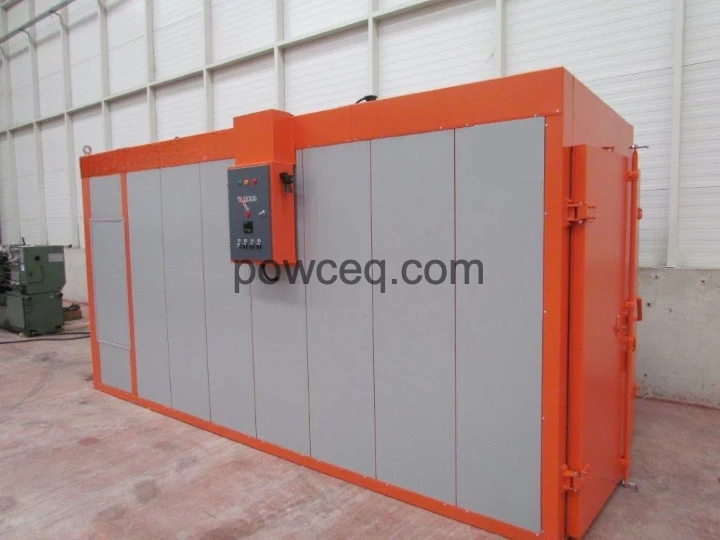 Nr.7 Oven gas G4
Nr.7 Oven gas G4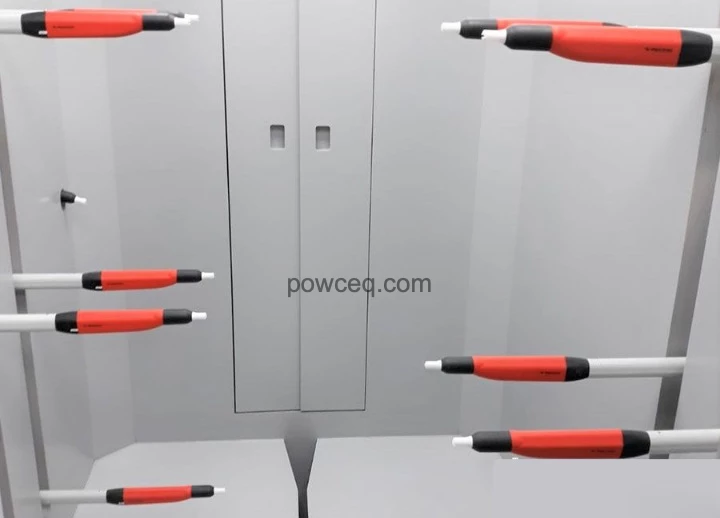 Automated Plant
Automated Plant Set of small booth + oven + gun
Set of small booth + oven + gun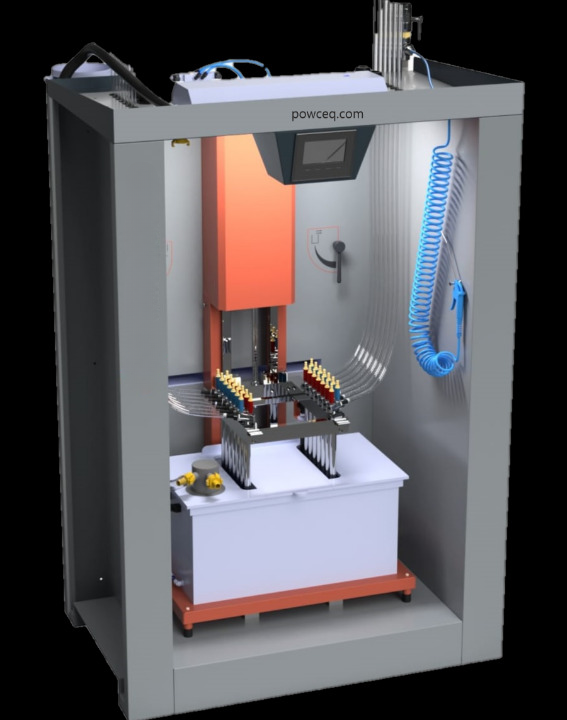 Powder center
Powder center User manual spray guns
User manual spray guns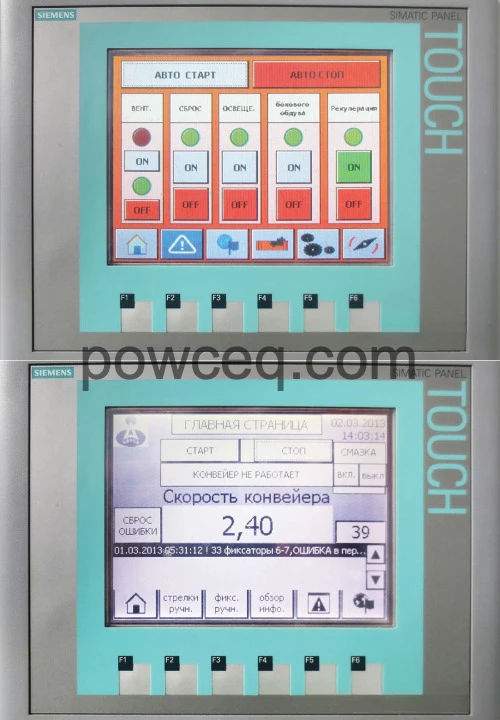 User manual booth
User manual booth User manual oven
User manual oven Atex-Certificate
Atex-Certificate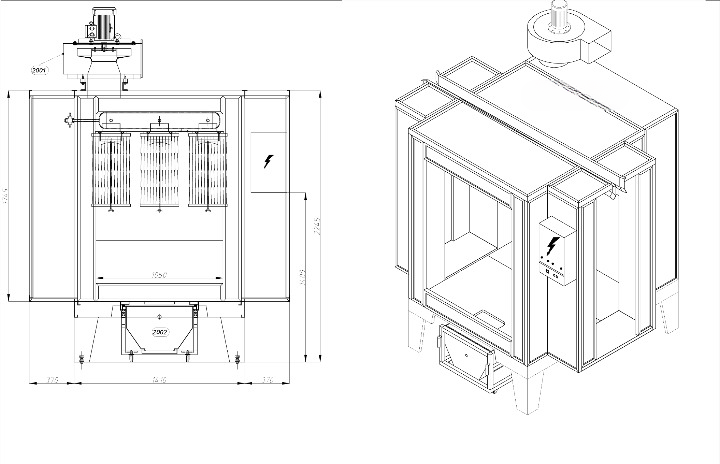 Dimensions booths
Dimensions booths